The application of single chip microcomputer is more and more common. Some microcontrollers have a serial communication port to make their application range even wider. For example, the serial port of the 51 series MCU is a full-duplex communication interface, which can transmit and receive at the same time, and can select multiple serial communication modes, including multi-machine communication, by setting the serial control register SCON. In practical applications, long-distance multi-machine serial communication is often involved.
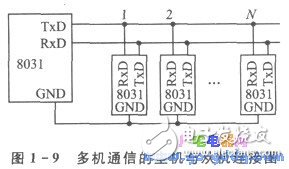
According to the general introduction, the host and slave of multi-machine communication are connected as shown in Figure 1-9. The communication mode is queried by the host and the slave responds through software programming. However, this communication mode is limited to the master and slave. Within a few meters). This is because the TTL level signal sent by the serial port TxD is not enough to realize long-distance serial data transmission in terms of driving capability and anti-interference ability, so it is necessary to realize long-distance communication of the serial port of the single chip (tens of meters to A few kilometers), we must find another way.
Long distance serial communication circuit1. Single-chip long-distance serial communication circuit
In order to realize long-distance serial communication of the single-chip microcomputer, a differential driver MC3487 and a differential receiver MC3486 are respectively added to the front end of the serial port TxD and RxD signals, and the variable level transmission and reception is differential transmission and reception. The multi-machine serial communication connection after adding the differential drive and differential receiving circuit is shown in Figure 1-10. The empty squares represent the added differential drive and receive circuits. As can be seen from the figure, after the differential drive and receiver are added, only the D+ and D_ data lines are left between the host and the slave. The master and the slave do not need to be connected in common, completely eliminating the long-distance ground potentials. The impact is caused and the cable is simplified. However, it is worth noting that the two transmission lines use twisted pairs to better eliminate electromagnetic interference. After the driver and receiver circuits are connected, the original communication program design is not affected.

The circuit and the single chip have three connection signals of TxD, RxD and GND, and the output has two data signals of D+ and D_. A 74LS04 NOT gate, an MC3487 differential driver and an MC3486 differential receiver are used in the circuit; capacitors C1 and C2 are the filter capacitors of the transmission lines D+ and D_, respectively, for filtering high-frequency interference of the system; Ri is the power of the D+ signal. Flat lifting resistor. The MC3487 and MC3486 are paired with excellent differential drive and receiver ICs that are electrically compliant with the RS-422 A standard for serial communications. It can be purchased in the market, and the price is not high (domestic models are DS3487 and DS3486 respectively).
The pins of the MC3487 are shown in Figure 1-4, and the truth tables are listed in Table 1-6. It is a four-RS-422 A transmission line driver with three-state output, pin 1 is the input of the first driver; pin 2, pin 3 is the in-phase, inverting output of the first driver, and the output is controlled by pin 4. When pin 4 is low, output pin 2 and pin 3 are in a high impedance state. The MC3486 is a quad differential line receiver with a three-state output. Pins 1 and 2 are the inverting and non-inverting inputs of the first differential receiver. Pin 3 is the output and the output is affected by the pin 4. control. When pin 4 is tied high, the output is allowed.
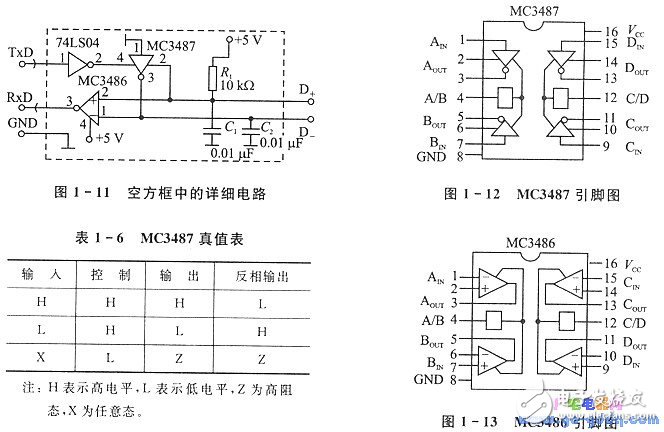
Now let's analyze the working process of the differential drive receiving circuit in Figure 1-11. Take the serial port transmission data as an example. When TxD sends a low level, it is added to the control terminal 4 of MC3487 after being inverted by 74LS04. Input pin 1 is fixed to ground and is low. It can be seen from Table 1-6 that at this time, the output pin 2 is at a low level, the pin 3 is at a high level, and the signals of the feet 2 and 3 are respectively sent to the remote differential driver and receiver via the transmission lines D+ and D_. At this time, the far-end receiving MC3486 pin 2 (corresponding to D+) is received as a low level, and pin 1 (corresponding to D_) is received as a high level, that is, the op amp non-inverting input is low, and the inverting input is High level. Therefore, the output pin 3 is at a low level, that is, the signal received by the remote MCU RxD is consistent with the low level emitted by the transmitting terminal TxD. When TxD sends a high level, it is inverted by the control pin 4 to a low level. At this time, the output pin 2 and the pin 3 are in a high impedance state, which is equivalent to floating. At this time, the remote receiver receives a level pull-up resistor due to D+, so D+ is high level, and D_ is low level, that is, the input terminal 2 of the remote receiving MC3486 is high level, and the foot 1 is low. Level, output pin 3 is high. It can be seen from the above analysis that the signal level received by the remote RxD is completely the level of the transmitting terminal TxD, that is, the level state of the serial communication port of the receiving/transmitting terminal of the single chip does not change. Because the MC3487 has strong line drive capability and the differential level reception of the MC3486, the data transmission distance is greatly extended, and the influence of the ground potential of the common ground system is eliminated.
Zysen offer RF Reflective Type Switches, 2 to 16-way, controlled by TTL, minimum isolation 60dB. Customized frequency and optimized specifications available. Contact us with your requirement.
Reflective Switches,Microwave Pin Diode,High Frequency Switch,High Frequency Switching Transistor
Chengdu Zysen Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.zysenmw.com