We often use AS SSD Benchmark software when testing SSD. Through this software, you can get a general understanding of the reading and writing of some SSDs. However, some highly demanding friends can judge the performance of SSD through the 4K read and write performance tested by this software.
Today we are going to learn about the AS SSD Benchmark software and the so-called "4K performance".
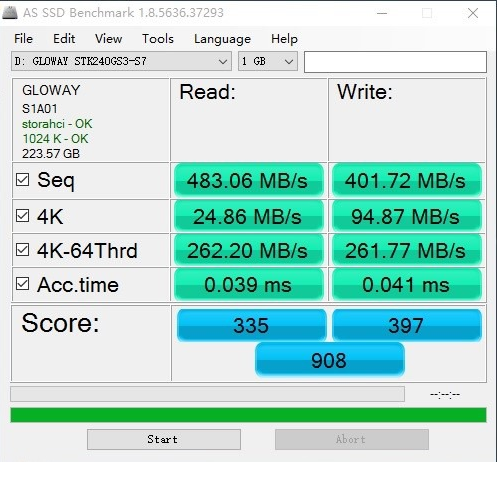
The read and write performance of Guangwei Zhanjiang is not bad, right?
AS SSD Benchmark is a software used by many of us to measure SSD speed. But many of us just look at the test data, but don't understand the meaning of each test item, let alone the reading and writing methods of SSD, application methods, etc., which caused some misunderstandings.
Let's first understand the specific meaning of several test items of AS SSD Benchmark:
1. Seq (continuous read and write): AS SSD will first continue to write to the tested partition with the size of 16MB as the unit, generate a file up to 1GB in size, and then read the file with the same unit size, and finally Calculate the average grade and give the result. The test file will be deleted immediately after the test.
2. 4K (4k single queue depth): it is a random single queue depth test. The test software generates a 1GB test file with a unit size of 512KB, and then performs a random 4KB unit size to write and write in its address range (LBA). Read the test until you run through this range, and finally calculate the average score to give the result. Due to the generation steps, this test will produce a total of 2GB of data written to the hard disk, and the files will be temporarily retained after the test is completed;
3. 4K-64Thrd (4k 64 queue depth): it is a random 64 queue depth test, the software will generate 64 test files of 16MB size (total 1GB), and then simultaneously perform 4KB unit size in these 64 files Write and read, and finally take the average score as the result, resulting in a 2GB data write volume. After the test is completed, the tested file will be deleted immediately;
4. Acc.TIme (access time): the data access time test, randomly read the entire disk address range (LBA) with 4KB as the unit size, and 512B as the write unit size, and randomly write to the reserved 1GB address range, Finally, the test result is given with the average score.
5. Score: Omitted. There is nothing to say.
Most novices look at the continuous reading and writing speed when testing. And Xiaobai, who has a higher rating, looks at 4K and 4K-64Thrd, and looks at the so-called "4K performance" to judge the quality of SSD.
Let's first understand what 4K is.
4K is a bomb when fighting the landlord. Among SSDs, 4K is the smallest read and write unit of SSDs. For example, if we need to write a 2K data, we actually have to write 4K; if we need to write 13K data, we have to write 16K data (the write amplification factor is not considered here). It seems that the data we write is composed of countless 4K. 4K performance includes 4K random and continuous read and write performance. The quality of 4K performance also shows the read and write performance of SSD. Therefore, testing of 4K performance is necessary.
But the source of the "4K performance" we often say is AS SSD Benchmark, which is narrowly defined. In fact, it is 4K random read and write performance, which represents the data throughput capacity of the hard disk (in iops), which is opposite to continuous read and write performance. So what is continuous read and write performance and random read and write performance? Continuous read and write performance is the performance of sequential reads and writes, while random read and write performance is the performance of random reads within a range. Random read and write, large range, and scattered. When our SSD is used for the first time, it is written sequentially, but as the use time is longer and the capacity increases, its writing will become more scattered. Therefore, testing the 4K random read and write performance helps us understand the read and write performance of the SSD, and the stability of the performance.
In daily applications, web page cache writing, system file update, including program, game loading, response, etc. are closely related to random 4K read and write performance. It can be said that the speed of 4K read and write determines the operating experience of the system.
So 4K performance is very important.
However, as we said above, the "4K performance" measured by AS SSD Benchmark is the random read and write performance of single queue and 64 queue depth. However, it is impossible for the applications we use daily to perform random reads and writes under a pure single queue depth, and it is also impossible to always reach 32 or 64 queue depths (this kind of depth is generally used on servers). In a small office environment, random reads and writes with a queue depth of 4-16 are generally the mainstay. Therefore, the two random 4K performances measured by ASS SSD (single queue and 64 queue) are of little significance in an ordinary home environment. The 4K random read and write performance measured by AS SSD Benchmark is too one-sided.
In addition, SSD performance includes read and write performance and security performance. The read and write performance of SSD includes continuous read and write performance and random read and write performance. Therefore, judging the read and write performance of an SSD based on a random read and write performance alone, or even judge the performance of an SSD, is one-sided and narrow.
In general, 4K performance is important, but the narrow "4K performance" measured by AS SSD Benchmark is not very important and is for reference only. Therefore, it is unreliable to judge the performance of SSD based on the so-called "4K performance" measured by AS SSD Benchmark alone!
Having reached this conclusion, some patients with 4K theory said that "group RAID0, 4K random performance has not increased, so the read and write performance of hard disk array has not increased, group RAID0 is useless" This question also has an answer.
Why is the continuous read and write performance greatly improved after RAID0 is set, but 4K randomly drops? After the SSD is formed into a RAID array hard disk, it is equivalent to that the SSD becomes larger. When the SSD becomes larger and there are more channels, the random range is also larger and scattered. Therefore, after the group RAID0, 4K random read and write does not increase but decrease. The continuous read and write performance is greatly improved because the SSD itself is a NAND array, and the RAID0 array composed of SSDs is equivalent to a new, larger-capacity, multi-channel SSD. Keeping RAID0 hard disks with sufficient available capacity during use, just like using SSDs, is conducive to continuous read and write performance, and it is also conducive to maintaining high read and write performance of hard disks.
It simply explains why the 4K random read and write performance of the hard disk after group RIAD0 does not increase but declines, and also simply explains whether group RAID0 is useful for improving the read and write speed. It can't be too complicated, after all, I am not a professional engineer. There is no need to be too complicated, because although using SSD group RAID0 to increase the speed, but the cost is too high.
Asgart recently released a NVMe SSD, AN Series M.2 SSD, using 3D NAND, SMI2260 master control, entry-level, the first cheapest in China. Its performance exceeds Intel 600P. Its read and write performance is 1850M/S and 850M/S respectively. It is almost twice as fast as the more expensive 600P, and twice as fast as the Samsung 850EVO, the SSD sales champion at almost the same price. And this model is very careful in the temperature control, even the main control has a heat sink, the temperature is about 600P. (Some people say why the heat sink is here, do you want to wrap the roast duck? Lazy to deal with it. Next time I will talk about the heat sink.) As for the price, go to a certain place.
With Asgart AN Series M.2 SSD, use SSD to set RAID0, use HDD to set RAID0, use RST technology to accelerate, etc., those painstaking efforts, don't mention the past.
There are too many ups and downs in life, and the same goes for the SSD market. A group of foreign brands have made ups and downs and pushed up the price of SSDs. But life has to go on. In "Let the Bullets Fly," Ge You said, "The bandits must be suppressed, not suppressed." The same is true for SSDs. As the bottleneck of computer speed, SSDs must be available, and they cannot be upgraded without upgrading NVMe SSDs. With Asgart AN Series M.2 SSD, let’s not worry, let the computer fly for a while.
The read and write performance of NVMe SSD far exceeds that of SATA SSD. It can be said that the emergence of Asgart's super cost-effective AN Series M.2 SSD makes SATA SSD nowhere to go.
Look at the mainstream battle between entry-level NVMe SSDs represented by Asgart AN Series M.2 SSD and mainstream SATA SSDs. See "Let the Bullets Fly" in the SSD industry.
SATA SSDs are so expensive anyway, we plan to use NVMe SSDs directly. For SATA SSD.
Immersion Cooling is a technique used to cool components of IT equipment that consists of submerging the computer components in a thermally conductive and dielectric liquid. Through this practice, the servers are cooled and heat is transferred from the source to the liquid.
When we talk about Immersion Cooling, we also need to discuss the different types of Immersion Cooling, as well as the applications of Immersion cooling. The practice of Immersion Cooling has a multitude of benefits particularly as it allows datacenters to be managed in a greener and more sustainable manner. Environmental concerns has been a huge catalyst for the adoption of the technology in recent years.
deionized water
mineral oil
fluorocarbon-based fluids
synthetic
Immersion Cooling systems used to have a higher fluid cost than water cooling, but this is already changing.
A wide variety of liquids exist for this purpose, the most suitable being transformer oils and other electrical cooling oils. Non-purpose oils, including cooking, motor and silicone oils, have been successfully used for cooling personal computers
water cooling,oil cooling,immersion cooling box,liquid immersion cooling,apw12 power supply
Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ylhm-tech.com