0 Preface
The rapid development of commercialized high-brightness white LEDs (HBW-LEDs, hereinafter referred to as LEDs) with luminous efficiencies greater than 100 lm/W brings unprecedented opportunities for the fourth generation of lighting, and is a broad application. A road lighting source with excellent prospects and performance.
Nevertheless, it should be noted that in actual use, people not only have higher requirements for the on-site environment, lighting comfort and lighting energy saving of road lighting, but also LED street lighting sources with rich variety and high power. The light output characteristics are also different. Mainly reflected in the following two aspects: First, the diversity of road lighting environment, that is, the full power output from a single lighting period to the output of variable light intensity according to different periods of demand; the second is the requirements for road lighting energy saving, That is, from full-power lighting throughout the lighting period to de-powering lighting in certain periods, it can meet the requirements of road safety and save a lot of energy.
Therefore, for the above two points, special research is needed on the dimming scheme of the LED road illumination source in different illumination modes.
1 Analysis of dimming characteristics of LED road lamps
Whether from the current road lighting perspective or energy saving considerations, the dimming requirements of LED road lighting are reasonable and necessary. Due to the inherent characteristics of the LED device, the problem of dimming is not only a single change in the reduction in light output, but also a series of associated characteristic changes. The main interrelationships are the temperature rise of the LED chip, the light extraction efficiency, the change of service life, the light output characteristics of the illumination source, the lighting effect of the road, the operating characteristics of the driver, and the change of life.
1. 1 dimming mode of LED road lighting source
From the point of view of practical use, the dimming mode of LED road lighting source is mainly divided into two types: grading type and meta-level type. The specific analysis is as follows:
1. 1. 1 LED's stepped dimming mode
LED-level dimming is the most common and the simplest and most convenient dimming method.
In view of the relatively small power of the monolithic packaged LED and the limitation of the overall heat dissipation of the light source, the LED road illumination source generally adopts a multi-cell array structure. Each LED unit has an independent light distribution characteristic, which is the simplest form of unit group dimming under the cooperation of the output system of the driver, or the dimming mode of the street lamp interval illumination which is based on the traditional road lighting dimming method. . Not only that, but according to the influence of LED road lighting source dimming on its light output characteristics, it can be subdivided into the following categories:
(1) Uniform group dimming of LED units
For an LED unit with light output characteristics that meet the requirements of road illumination, uniform group dimming only changes the light output intensity of the road illumination source, and the characteristics of its light output are hardly changed, so that uniform light output characteristics before and after dimming can be obtained. Is a relatively good way of dimming. With the cooperation of the driver, multiple gear dimming can be realized.
Figure 1 shows the dimming principle of a multi-cell LED (in the case of a single LED unit with lens distribution to meet the requirements of light distribution characteristics) in the same road illumination source, and the uniform arrangement of LED units in the light source. Structure diagram (a style). It can be concluded that the contrast before and after dimming only changes the size of the light intensity output of the light source without changing its own light distribution characteristics. Therefore, the effect of dimming is ideal, but the smoothness of the brightness is slightly poor, and it cannot be arbitrarily adjust.
(2) Non-uniform group dimming of LED units
The non-uniform group dimming of the LED unit in the same road light source is mainly that each of the LED units has different light output roles, and the overall function is to form a light output characteristic that satisfies the light distribution requirement, and has the advantages of simple composition and convenient operation. . The road lighting effect in the dimming mode that needs to be emphasized or guaranteed is obtained by the non-uniform grouping of LED units. Figure 2 shows the dimming principle and the changes in the LED unit group before and after dimming. For example, in the middle and rear of the city road lighting, different lighting modes are required: the first half of the night and the secondary lane full lighting mode (group 1 + group 2) to ensure the traffic safety of the main/fast lane and the secondary/slow lane; The traffic flow in the second half of the night is very small, only the road lighting mode of the main/fast lane (group 2).
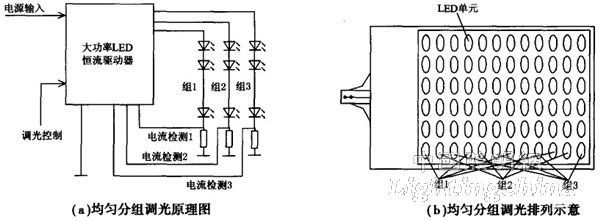
Figure 1 LED unit uniform group dimming principle and arrangement
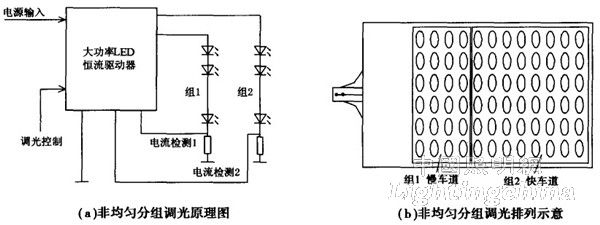
Figure 2: Non-uniform group dimming principle and arrangement of LED units
It can be seen that this dimming method is more simple and clear than that of Figure 1 under the same illumination source power.
(3) Interval dimming of LED road light source
The interval dimming of LED road illumination sources is a dimming mode of traditional road lighting (such as HPS street lamps). The purpose of dimming and dimming is achieved by opening and closing the separated light sources. The method is simple and convenient to operate. Although the light output characteristics of a single light source, the lighting effect, the heat generation of the chip, the light extraction efficiency, the service life, the driver characteristics, and the service life are not changed before and after dimming, and high energy saving effects (50%) can be obtained, but Its fatal shortcoming is that it has a great influence on the illumination uniformity of the overall road lighting, and it is easy to form a dark area of ​​illumination, the so-called "zebra effect", which seriously affects the road safety of the road and does not meet the national requirements for road lighting. It is only suitable for use on secondary/slow lanes and trails where lighting requirements are not critical.
1.1. 2 LED stepless dimming mode
The stepless dimming method of LED road lighting is an ideal dimming method that is freely smooth within a certain range. The main feature is that the working state of each D unit participating in the dimming is no longer only the two states of light and extinguish, but an intermediate link working in it, and the four D unit smoothly changes the working state as needed. The light flux output from the light source is freely changed over a wide range, and good road illumination, dimming, and energy saving effects can be obtained.
(1) Stepless linear dimming of LED
The stepless linear dimming of the LED is based on the constant voltage driver, and the magnitude of the output current of the driver is changed by the linear element connected in series at its output, that is, the brightness of the LED unit is adjusted. There are two ways to construct: one is a series of adjustable resistors (manual adjustment, see Figure 3 (a)), and the other is a series of high-power transistors operating in the amplification region (which can be adjusted with small signals). From the correspondence between the forward current of the LED and the light output, this corresponding relationship is almost linear within the allowable range. Figure 3 shows the principle and corresponding relationship of linear dimming of such an LED.
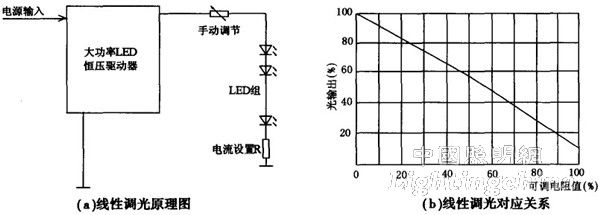
Figure 3 LED no group linear dimming principle and its correspondence
The main problem of this scheme is: based on the characteristics of white LEDs, the color temperature will change when dimming, it is not suitable for illumination sources with constant color temperature requirements, but it may have little effect on less important road lighting. Need to be carefully considered. In addition, the linear components at the output end will lead to an increase in overall loss and a decrease in efficiency. Therefore, it is not an ideal and good effect road lighting dimming solution.
(2) Stepless analog dimming of LED
LED's meta-level analog dimming is based on constant current driving conditions. By changing the output current of the driver by DC control voltage (such as 0-10 V) or resistor at the control end of the driver, it can also be adjusted. The luminous intensity of the LED unit of the road illumination is approximately linear, and the relationship between the dimming principle, the light output and the resistance value can be seen in FIG. 4 . The utility model has the advantages of simple circuit, small overshoot of current when adjusting, and relatively high efficiency. The main problem is that the color temperature at the time of dimming will also change, which is not suitable for illumination sources with constant color temperature requirements, but may have little effect on less important road illumination. Therefore, it is an ideal road lighting dimming solution with better effect.
(3) PWM type stepless dimming of LED
In order to solve the many unfavorable problems brought by the above dimming scheme, improve the effect of LED road lighting and the efficiency of dimming operation, by using the temporary visual characteristics of the human eye, without changing the magnitude of the instantaneous current of the LED, only Changing the duty cycle of the output current (ie, the current rms value changes) to achieve the purpose of dimming is an ideal dimming method. The relationship of dimming can be expressed as
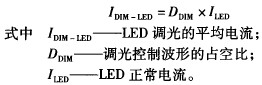
Figure 5 shows the specific application principle, the corresponding relationship between the light output and the duty cycle of the dimming signal, which can be used for reference.
The main advantage is that based on the characteristics of white LEDs, the color temperature of the light source will remain unchanged during dimming, so the effect on road lighting is more favorable; the disadvantage is that the overshoot current of the LED is large during dimming operation. The luminous efficiency is reduced and the entire circuit is more complicated.
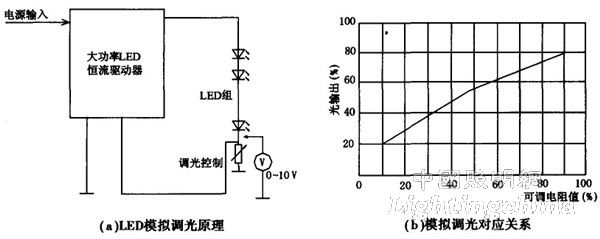
Figure 4 LED stepless analog dimming principle and corresponding relationship

Figure 5 PWM PWM dimming principle and corresponding relationship
(4) Phase-controlled dimming of LED AC input
It is also a feasible solution to adjust the luminous flux of the LED illumination source by changing the input voltage of the driver by using the AC phase modulation principle, and it is versatile. The most commonly used dimming scheme for self-illuminating lamps is achieved by relying on a mature component thyristor SCR to change the input AC voltage, but directly using the thyristor SCR to dim the LED will have the following problems:
First, the power factor of the light source, the smaller the conduction angle of the SCR, the lower the power factor. When the brightness is adjusted to 114, the power factor will be lower than 0.25. The second is the efficiency of the light source and the illumination effect. When the point is low, the LED current is insufficient, which will cause the SCR to be turned off early, causing the time of the RC delay circuit in the SCR dimmer to be disordered, causing the LED illumination source to flicker.
To this end, it is necessary to develop a driver chip that can be applied to SCR dimming dedicated LED illumination source to meet the dimming requirements of LED illumination sources using conventional SCR dimmers. References [4], [5] give the principle of this application, the corresponding relationship between the light output and the input power (see Figure 6).

Figure 6 AC input phase control dimming principle and corresponding relationship
1.2 Dimming characteristics of LED road lighting
It can be seen from the above analysis that the dimming problem of the LED illumination source not only causes a single change in the reduction of the light output, but also brings a series of related characteristic changes to the LED and the entire illumination source, so it is necessary to separately dim the operation thereof. Characteristics are studied.
1. 2.1 LED characteristics change
Since the mechanism of dimming LEDs is to change the magnitude of their forward current RMS, and many of the characteristics of LEDs are directly related to them, the characteristics of LEDs in dimming mode are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
(1) LED light output and light extraction efficiency
At present, the working principle of mainstream, high-power white LEDs for illumination is to use white LEDs to excite YAG phosphors to obtain white light. Literature [6] gives the relationship between the forward current of a brand of blue LED (InGaN) and the light output and light extraction efficiency.
It can be seen from Fig. 7 that the light output of the blue LED increases linearly with the increase of the forward current, which indicates that the current magnitude is proportional to the light output, and the light effect η=φ/W(lm/W) The forward current increases and decreases approximately linearly, because a considerable amount of energy is converted into heat by the lattice absorption, and does not play its due role. It can be seen that since the LED of the road illumination is in the dimming operation mode, the reduction of the current will bring about a decrease in the light output and an increase in the light extraction efficiency, which is advantageous for the operation of the LED road illumination. It is further inferred that for the above-mentioned road lighting mode in which the dimming operation is performed by changing the LED forward current, the operation of the LED in the illumination source will also be under favorable operating conditions; for the LED using the PWM mode for dimming due to discontinuity The operating mode is also beneficial for improving the operating conditions of the LED.
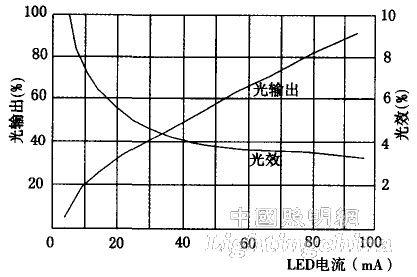
Figure 7 Correspondence between LED current and light output and light efficiency