Wallace Sabine, a pioneer in room acoustics research in 1922, came up with the formula: RT60=k(V/Sa)
The k value is a constant, k is equal to 0.161 when using metric units, and k is equal to 0.049 when using feet.
Sa (short for sabins) is the sum of the absorption coefficients of the various absorbing surfaces in the room. Different materials have different absorption frequencies, which can be calculated experimentally.
V is the volume of the room.
Here is the RT60 system on a page from New York University. The author is Piotr Filipowski. I put the code below. You can also calculate your studio, the reverberation of the small recording room at home. The value of time (RT60). Thanks to Piotr Filipowski for the simple statistics page.
Enter the size of the house, as well as the indoor items, the system will automatically calculate the value of RT60 at the corresponding frequency.
So what can we do with the calculated value of RT60? Suppose we have such a room, 6 meters long, 5 meters wide and 2.4 meters high. The ground, ceiling and walls are colored concrete.
In such a room, we gave him a few typical decorations, first carpeting, thick steps on the front and back walls, and light steps on the other walls and ceilings.
The initial room was a relatively straight reverberant line (blue in the picture below), and the reverberation time for each frequency band was about 8 seconds or so, and the sound would be very bright. When we changed the room according to the above scheme and changed a lot (red in the figure below), the reverberation time of 125 Hz became longer and the relative time of 4 kHz was shorter. Because the reverberation in the high frequency band has become a little smaller, some people will say that this room is too "dead", but it is not. He just "sudden" a little bit at high frequencies. The frequencies below 500 Hz have been improved.
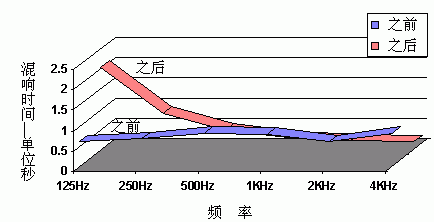
This is the mistake everyone loves to make. You can't concentrate all your attention on the high frequency area. You have to think about all the frequencies in the room. At high frequencies, the reverberation time of 0.3 seconds is reasonable. If it is 0.4 to 0.5, it is unreasonable. You must let them down. As shown in the figure, 125 Hz is 2 seconds, 250 Hz is 0.92 seconds, 500 Hz is reduced to 0.49 seconds, and it is reasonable to continue to drop to 0.3 seconds at 1000 Hz and finally to 0.21 seconds at 4 kHz. Don't just focus on high frequencies!
Transient voltage suppression diode, also known as a TVS diode, is a protective electronic component that protects electrical equipment from voltage spikes introduced by wires.
TVS diodes are placed in parallel with the circuit to be protected. When its voltage exceeds the burst breakdown level, excessive current is directly shunted. TVS diodes are clamps that suppress excessive voltages that exceed their breakdown voltage. When the overvoltage disappears, the TVS diode automatically resets and absorbs much more energy than a similarly rated crowbar circuit.
TVS,TVS DIODE,Transient voltage suppression diode
Changzhou Changyuan Electronic Co., Ltd. , https://www.cydiode.com